
In this article we will look at:
- What is breast cancer?
- How does breast cancer occur?
- Who is prone to breast cancer?
- What are the symptoms of breast cancer?
- How is breast cancer diagnosed?
- What are the complications of breast cancer?
- What is the treatment for breast cancer?
What is breast cancer?
Breast cancer is the most common form of cancer amongst women in India. It occurs very rarely in men.Breast cancer accounts for 16% of all female cancers and 22.9% of invasive cancers in women. It is responsible for 18.2% of all cancer deaths worldwide, both male and female.
Regular breast examination is very necessary to detect any abnormality right at the outset.
If you detect any abnormalities during a self-examination of your breasts you need to contact your family physician or a general physician without delay.
Depending on the results of further examination, your doctor may refer you to an oncologist.
How does breast cancer occur?
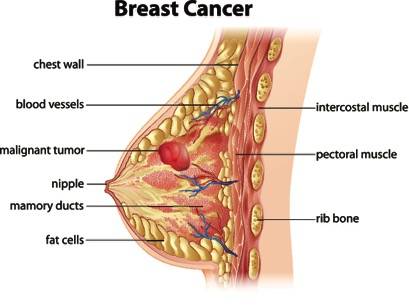
The cancerous tumour starts from one abnormal cell, usually in the inner lining of the milk ducts or lobules in the breast. If it is diagnosed when the cancerous cells are still within the duct or lobule, it is known as Ductal Carcinoma In Situ (DCIS), which is the most common type of non-invasive breast cancer. One in five new breast cancer cases is DCIS. A carcinoma in situ is easier to treat.
Unfortunately, most breast cancers are diagnosed when the tumour has spread from within a duct into the surrounding breast tissue. This is known as invasive breast cancer.Invasive breast cancer is further divided into:
- One where cancer cells have invaded the lymphatic vessels
- One where the cancer cells have not yet invaded the lymphatic vessels
Who is prone to breast cancer?
You’re at a risk of developing breast cancer if you:- are a woman older than 50 years
- have already had cancer in one breast
- have a family history of breast cancer
- have inherited certain gene mutations (such as BRCA1 and BRCA2 - which account for 5% - 10 % of breast cancer cases). This has been much in the news of late and has also been nicknamed as the “Jolie effect” after Angelina Jolie, the Hollywood actress who highlighted how genetic testing can prevent breast cancer.
- have been exposed to chest radiation for any treatment during your childhood years, or before menopause
- began menstruating before 12 years of age
- had your first child after the age of 29 years, or if you do not have a child at all. The opposite is true if you have a family history of breast cancer. Meaning if you have a family history of breast cancer your risk will be minimized if your first child is born after 29 years or if you do not have any child at all.
- undergo menopause after the age of 54 years
- have a higher breast density
What are the symptoms of breast cancer? How is breast cancer diagnosed?
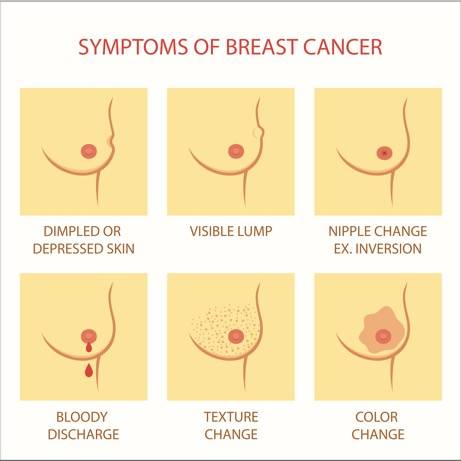
The vital symptoms of breast cancer include:
- A painless lump in the breast, near the collarbone, or under the arm ( however, not all lumps are cancerous, some are benign)
- Nipple tenderness or changes in the shape of the nipple, such as an inverted nipple
- Breast pain which does not go away after your next period
- Skin of the breast, nipple, or areola suddenly becoming tender, or itchy, or scaly, or sore, or red
- Sudden asymmetry of breasts such as sudden swelling of a breast, or sudden shrinking of a breast
- Nipple discharge from one of the breasts which can be clear or bloody
Diagnosis
After asking you about your symptoms, the doctor will thoroughly examine your breasts for any lumps, or any changes in the skin texture, and changes in the nipples.If the symptoms are found to be positive the doctor will suggest imaging tests to find out what is going on inside your body, such as:
- Mammograms: which is an x-ray of the breast and helps to detect any abnormalities in the breast.
- Breast Ultrasound: is often used to check any abnormal results of a mammogram. An ultrasound reveals whether the breast lump is filled with fluid ( cyst) or it is a solid lump.
- Biopsies: wherein, tissues are removed from the suspicious area, and are examined under a microscope. The tissue is further tested to find out if it is cancerous.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): is a procedure in which large magnets and radio frequencies are used to search for cancer. MRI does not use X - rays so, there is no radiation exposure. This captures multiple images of breast tissue n the inside.
- Ductogram: is used to identify the cause of nipple discharge.
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): is a
What are the complications of breast cancer?
Breast cancer surgery, though considered safe, may give rise to a number of complications.Psychological complications include:
- fear
- anxiety
- loss of sleep
- loss of sexual interest
- depression due to possible physical changes resulting from the intensive treatments
- inflamed lung tissue
- heart damage
- secondary cancers
- hematoma or buildup of blood under your skin
- seroma or buildup of fluid on the site of the surgery
- lymphedema or swelling of the arm on the side of the surgery
- reactions to the anesthesia
- low immunity 7-14 days after undergoing chemotherapy and thus prone to infections
- hair loss and thinning due to chemotherapy
- nausea and vomiting episodes after chemotherapy
- constipation or diarrhoea
- dental and mouth problems, such as sore gums, mouth ulcers
- dry skin and brittle nails
- constant exhaustion
- infertility
- early menopause
- menopausal symptoms (hot flashes and vaginal symptoms)
What is the treatment for breast cancer?
Medical treatmentsDepending on the type and stage of your breast cancer, there are several ways to treat it such as:
- Surgery
- Radiation therapy
- Chemotherapy
- Hormone therapy
- Targeted therapy
Exercise
Research shows exercise is safe during and after cancer treatment. It can strengthen your physical body. And the stronger you are before surgery, the quicker you can recover from it.Before you decide to start on an exercise regimen, it will be wise to consult with your doctor and find out what kind of exercises suit you the most.
You may need the help of a physical therapist if you have never exercised before.
No comments:
Post a Comment